Whatsapp/Linkedin/Google
Temporary Works Info & Example Designs
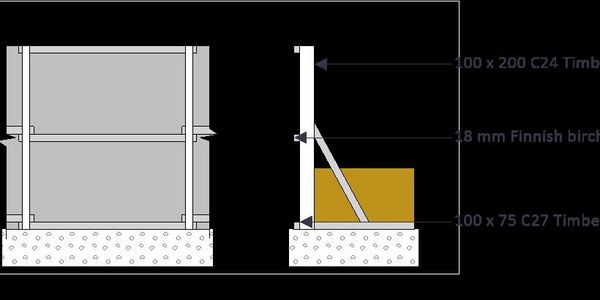
Hoardings & Fencing
Hoardings are typically made of sturdy materials like plywood, metal panels, or reinforced plastic sheets. They are designed to be durable, weather-resistant, and capable of withstanding the rigors of a construction site. Local regulations and building codes often govern the requirements for hoardings, including their dimensions, structural stability, and safety features.
Excavations/Earthworks/Trenching/Stockpiles
Construction professionals typically conduct geotechnical assessments, We will design appropriate excavation supports or shoring systems, and implement erosion and sediment control measures to ensure the safety and sustainability of these operations. Additionally, local regulations and permits may be required for excavation, earthworks, trenching, and stockpile activities to comply with legal and environmental requirements.
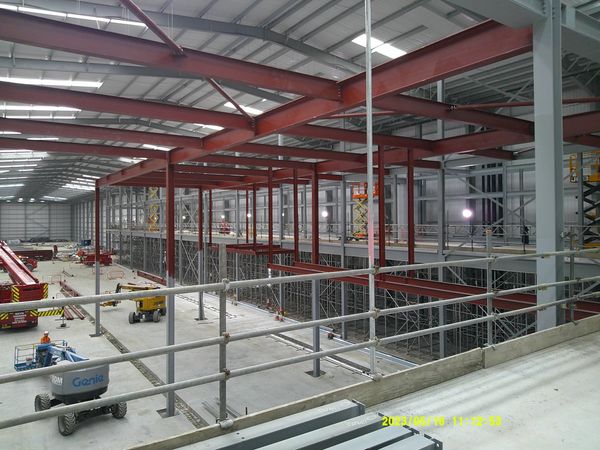

Structures/Propping/Needling/Falsework/Steel Frame
Propping: Propping involves the installation of temporary supports, such as steel beams or scaffolding, to provide additional structural stability to a building or structure. Propping is typically used when alterations, repairs, or modifications are being made to existing structures, or when supporting walls or columns are removed temporarily for construction purposes.
Shoring: Shoring refers to installing temporary vertical supports, often in the form of hydraulic or mechanical jacks, to support excavations or existing structures. Shoring is commonly employed to prevent soil movement or collapse during construction, particularly in deep excavations or when working in unstable soil conditions. It helps to ensure the safety of workers and nearby structures.
Needling: Needling is a technique used to provide temporary support to a structure when an opening, such as a doorway or window, needs to be created or enlarged. It involves placing temporary beams (needles or strongbacks) across the opening to distribute the loads from the structure above. Needling allows construction work to proceed while maintaining the structural integrity of the building.
These techniques require careful planning, engineering calculations, and consideration of the specific project requirements. We with your construction teams assess the structural requirements, soil conditions, and loads involved to determine the appropriate propping, shoring, or needling solutions. Compliance with safety regulations and guidelines are crucial to ensure the temporary supports' stability and the construction site's overall safety.

Method Statements & Risk Assessments (RAMS)
I am a professional with profound expertise in method statements and risk assessments within the construction industry. With an extensive background and years of experience. I can demonstrate a remarkable ability to develop comprehensive and meticulous method statements and risk assessments that meet the highest safety and compliance standards.
A risk assessment is a systematic process of identifying, assessing, and prioritizing potential hazards or risks associated with a particular activity, process, or situation. It involves evaluating the likelihood of an adverse event occurring and the potential consequences or impact it may have. Here's a general framework for conducting a risk assessment:
1. Identify Hazards: Identify potential hazards or sources of harm relevant to the activity or situation. This may include physical, chemical, biological, or ergonomic hazards.
2. Assess Risks: Evaluate the likelihood and severity of each identified hazard. This can be done through qualitative assessments (e.g., low, medium, high) or quantitative assessments (using numerical scales or probability calculations).
3. Determine Risk Level: Combine the likelihood and severity assessments to determine the overall risk level for each hazard. This helps prioritize risks and focus resources on those with the highest potential impact.
4. Control Measures: Identify and implement appropriate control measures to mitigate or eliminate the identified risks. This may include engineering controls, administrative controls, or personal protective equipment.
5. Evaluate Residual Risk: Assess the remaining or residual risk after implementing control measures. Determine if the residual risk is acceptable or if additional measures are needed.
6. Monitor and Review: Regularly monitor and review the effectiveness of the control measures and the overall risk management process. Make necessary adjustments and improvements as required.
7. Documentation: Document the risk assessment process, including the identified hazards, risk assessments, control measures, and any decisions or actions taken. This documentation helps demonstrate compliance and facilitates communication with stakeholders.
Please consult us to ensure industry standards ensure a thorough and effective risk assessment process.
DMTECS Temporary Works & Construction Safety Ltd
Norfolk, England, United Kingdom
Copyright © 2023 DMTECS Temporary Works & Construction Safety Ltd - All Rights Reserved.
Powered by GoDaddy

Announcement
Welcome & thanks for visiting my site. I started my own business to make the construction industry rules easier to navigate ensure you work safer & save money. Please contact me I would love to help you & you're business.